How to stick to your New Year’s fitness goals

Mastering New Year’s Fitness Goals
The confetti has settled, champagne sips are a distant memory, and those well-intentioned New Year's goals are staring back at us from sticky notes and fridge magnets. We've pledged to shed winter layers, build endurance, and finally claim that gym membership as our best friend. But amidst the enthusiasm, whispers of doubt creep in: can I really stick to this? How do I navigate the maze of conflicting fitness advice?
We're joined by the expertise of renowned celebrity fitness trainer Don Saladino, sharing his insights on how to optimize your performance and fuel your fitness journey.
Let's dive in.
1. Get to know your body
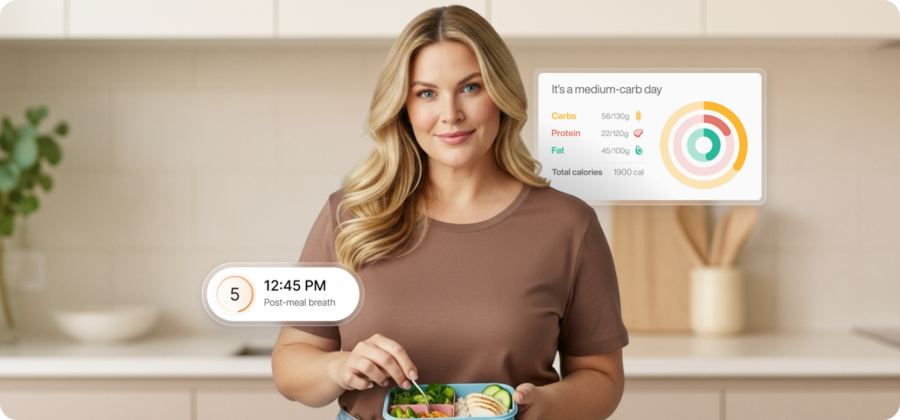
To achieve your fitness goals sustainably, a deeper understanding of your unique physiology is essential. There is no one-size-fits-all. Everyone's body is different and reacts differently to food and activities. This includes recognizing the importance of your body’s metabolism, specifically focusing on metabolic flexibility.
What is Metabolic Flexibility?
Metabolic flexibility is the ability of the body to efficiently switch between burning carbohydrates and fats for energy. This pivotal process is crucial for weight management and overall health.
When you are metabolically flexible, your body can effortlessly transition between fuel sources, optimizing energy utilization from various macronutrients like carbs and fats. Understanding your pre- and post-workout nutrition is essential, as it directly influences your metabolic flexibility and plays a significant role in achieving your fitness goals.


Carbohydrates are the Primary Source of Muscle Energy
In the fitness world, the role of nutrition, particularly carbohydrates, is often misunderstood. Far from being the enemy, carbs are, in fact, a powerhouse, especially for fueling up and maintaining energy during workouts.
Carbohydrates are a main source of energy for the body, breaking down into glucose, which is vital for cellular energy needs. During exercise, your body primarily relies on glucose from carbs for rapid energy production. This is where ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the primary energy molecule, comes into play. The process of glycolysis, occurring in the muscle cells, rapidly breaks down glucose to form ATP, providing the immediate energy muscles need for contraction.
The Role of GLUT4 in Glucose Uptake
Pre-workout carbohydrate consumption is pivotal for boosting energy levels. Meals or snacks rich in carbs ensure ample glucose availability for energy production during exercise, enhancing performance and endurance. This is facilitated by GLUT4, a glucose transporter in muscle and fat cells. Exercise stimulates the translocation of GLUT4 to the cell surface, enhancing glucose uptake into muscle cells, which is crucial for maintaining energy levels during workouts1.
Regular physical activity can lead to adaptations in muscle cells, such as increased numbers of mitochondria and improved insulin sensitivity. These adaptations enhance the muscles' ability to use carbohydrates more efficiently, providing better energy support during exercise.
2. Fuel your body, Pre-workout
The secret to crushing your New Year's fitness goals lies in what you do before you even step foot in the gym. Pre-workout nutrition is crucial in preparing your body with the necessary energy and nutrients for an effective workout. Tailoring your meal intake before engaging in activities such as strength training or high-intensity interval training makes the difference in ensuring your body has adequate fuel for both during and post-exercise.
Recent research2 indicates that the correct intake of nutrients before exercising can greatly enhance one's physical performance and endurance. The research also emphasizes the importance of a personalized diet plan and strategy that varies according to your sport, personal goals and food preferences.
Don, who knows a thing or two about peak performance, swears by proper pre-workout fueling. As he puts it, 'Carbs aren't the enemy! They're your teammates when it comes to crushing your workouts.'
"Carbs play a critical role. They help in retaining water, feeling full, and maintaining energy for effective training. It's important to manage carb intake correctly, as Lumen helps in recognizing carb-burning states, aiding in making informed decisions about food intake before workouts. This insight is invaluable for ensuring you have the right balance of fats and carbs for your workouts."
Don Saladino, Celebrity Fitness Trainer
By adopting consistent daily practices, such as
- monitoring your metabolic rate before exercising
- consuming the right quantity of food before your workout,
you can significantly improve your performance and outcomes.
Pre-workout meals that include carbohydrates also help optimize metabolism, enhance performance, and reduce fat oxidation3.
What are the benefits of pre-workout nutrition?
Improved Endurance: Consuming a nutritious snack or meal before exercising can help you to stay energized for a longer period, particularly when working out at a high intensity.
Better Muscle Recovery and Muscle Building: Since muscles are broken down during a workout, you must consume enough protein and carbohydrates to repair the tissue. This way, you avoid muscle damage, and it can heal and build properly.
Increased Metabolic Rate: Eating before a workout increases your metabolic rate, which helps burn more calories during your workout and extends throughout the day.
Helping Regulate Blood Sugar Levels: Consuming slow-absorption carbohydrates provides a steady source of energy that helps maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Improving Mental Focus: You can improve your mental focus by being alert, improving your memory, and concentrating on your workout.

How pre-workout nutrition impacts performance
When you consume a meal rich in carbohydrates, your body increases insulin production, which helps in the absorption and use of glucose for energy. This carb-loading aims to maximize your muscle's glycogen stores before endurance exercises lasting more than 90 minutes. This helps delay the onset of fatigue and enhances your performance.
When you're in a fasted state or during low carbohydrate intake, your body shifts to burning fats. This switch is essential for maintaining energy levels and supporting different bodily functions under varying dietary conditions.
Timing and Composition
The effectiveness of your workout is significantly influenced by your pre-workout nutrition. Timing your meals and snacks will vary depending on the workout you're planning to do. The last thing you want to do is overeat and feel full and uncomfortable before starting your workout. Consuming the right balance of carbohydrates before exercise ensures that you have enough energy to power through your session.
Consuming too many carbs without sufficient physical activity can lead to weight gain, while not consuming enough can lead to decreased performance and fatigue.
"In the short term, it's important not to enter the gym with low energy. Insufficient fuel can lead to low energy levels, digestive issues, and feeling lethargic. On the other hand, long-term nutrition affects overall health - think 'you are what you eat.' Proper eating, rest, and stress management can significantly improve health markers. It's a balance of eating right and making adjustments as needed."
Don Saladino, Celebrity Fitness Trainer
3. Make better nutritional decisions
Recent studies, such as the 2022 research published in the Journal of Sports Nutrition, align with Don's approach, highlighting the need for a balanced diet tailored to individual fitness goals and preferences.
Understand the role of different nutrients:
- Carbohydrates: Quick energy source, ideal for pre-workout.
- Proteins: Essential for muscle repair and growth.
- Fats: Provides sustained energy for longer workouts.

A pre-workout meal should ideally be rich in carbohydrates and moderate in protein and fats. This balance provides a sustained energy release, keeping you fueled throughout your workout. Simple carbohydrates are particularly useful as they are quickly digested and readily available as an energy source.
4. Overcome your Fitness Doubts: "Leave it to Lumen", according to Don
We cannot express it enough, personalization is crucial in nutrition. What works for one person may not work for another. With Lumen, you can measure your metabolic rate, which builds a personalized carb cycling meal plan based on your body's current needs and fuel levels for your selected workout. This level of personalization not only helps boost energy but also enhances your body’s metabolic rate, leading to more effective workouts and better overall health.
"It's crucial to customize your program to a level that's achievable and can be improved upon. Starting with something like Lumen and gradually enhancing it can be greatly beneficial."
Don Saladino, Celebrity Fitness Trainer
Don also explains how 'the key is to show progress and maintain a routine that builds confidence, which you can then expand upon later. The goal is to maintain this without feeling discouraged or losing motivation. As you see small victories, it boosts your motivation.'
For short and medium to high-intensity workouts, your muscles use mainly carbs for fuel.

Carbs are the preferred fuel source for high-intensity workouts because they are more fuel-efficient, meaning that your body gets more energy from carbs for a given amount of oxygen4.
So before you do a medium to high-intensity workout, it’s important to make sure you have enough available energy from carbs to optimize your workout.

Alternatively, low to moderate intensity workouts do not require carbs for improved performance. Fatty acids are the primary fuel source during low-intensity activity, like walking. Because fat reserves in the body are nearly unlimited, low-intensity activities are able to continue for a long time without large amounts of glycogen.
Taking a measurement with your Lumen before a workout can help you understand if you have enough carbs or need to consume more carbs to enhance performance.

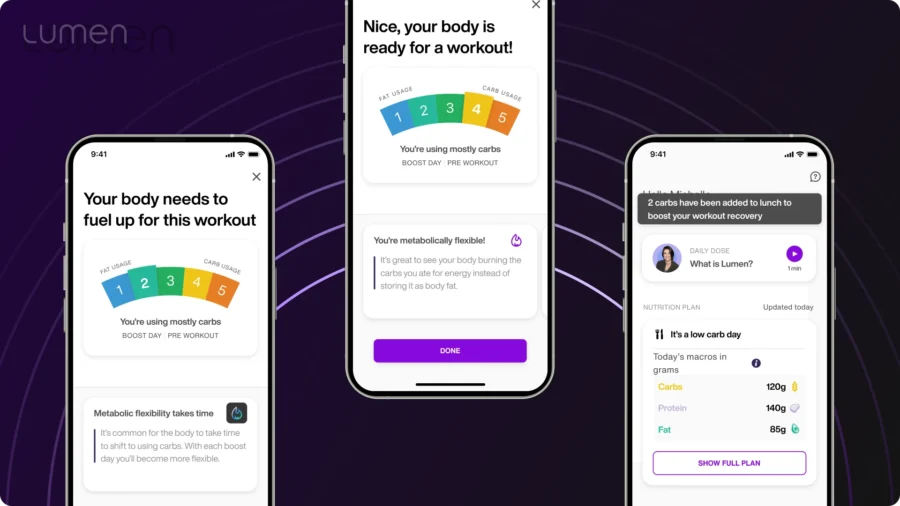
Did you shift to fat burn?
To see whether your body shifted toward using more fat after an intense workout, wait until your heart rate normalizes and for lactic acid buildup to clear your muscles. Lactic acid inflates the readings, and can cause inaccurate measurements.
The more intense a workout, the longer this may take. This could take as little as 20 minutes for some individuals, and for others up to 45 minutes. As a general rule, wait 30-40 minutes after a medium to high intensity workout to take a breath and measure your metabolism.
5. Prioritize sleep for peak performance
Think of sleep, stress, and your metabolism as a three-legged stool. If one leg is wobbly (like chronic stress), the whole thing gets shaky. That's why prioritizing good sleep and stress management is just as important as what you eat before a workout.
A lack of adequate sleep can have significant consequences, potentially leading to serious health issues such as diabetes and a heightened risk of heart disease.
Both the duration and quality of sleep play a critical role in maintaining metabolic health. Insufficient sleep, even for a short period, can cause a healthy individual to develop insulin resistance.
Poor sleep can adversely impact the body by:
- Altering hormone levels, leading to decreased leptin and increased ghrelin
- Contributing to inflammation
- Promoting insulin resistance
- Elevating the risk of chronic health issues
- Leading to weight gain
Maintaining proper sleep hygiene is crucial in enhancing metabolic flexibility. This is closely linked with effective stress management, which similarly affects metabolic health.
Stress triggers the release of hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol. During a “fight or flight” response, the body releases glucose to provide additional energy needed to handle the situation.
However, chronic stress can disrupt the way your body processes glucose, potentially causing conditions like hyperglycemia (too much sugar in your blood) or even reactive hypoglycemia (sudden drops in blood sugar). This excess glucose can, over time, increase the risk of developing long-term issues such as diabetes.
Working on reducing stress and sleeping better can help keep your sugar levels healthy and improve your body's metabolic flexibility.
"Sustainability lies in moderation - in training, intensity, and eating habits. It's about finding what keeps you consistently engaged in your training. Including a cheat meal as part of your routine can also help. It's all about maintaining a balance that feels right and keeps you motivated."
Don Saladino, Celebrity Fitness Trainer
Takeaways and Final Thoughts
Our discussion with Don Saladino reinforces the importance of a balanced, personalized approach to nutrition. By understanding your body's needs and incorporating tools like Lumen, you can set yourself up for a year of sustained fitness and health.
"By using Lumen's metabolic device for breathing to understand your fat or carb-burning state, I've optimized my energy levels, recovery, training effectiveness, and overall mood. It's not just about strength; it's about optimizing each day to continue building muscle while staying lean."
Don Saladino, Celebrity Fitness Trainer
Remember, it's not just about a New Year’s resolution; it's about a lifelong commitment to your health. Start today, and let your journey to a healthier, fitter you begin!







 Digital download
Digital download